Nutritional Guidance for Fitness: Fueling Your Goals
Nutritional guidance for fitness is a critical component of achieving your desired fitness goals. Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or just starting your fitness journey, understanding the role of nutrition in performance, recovery, and overall well-being is essential. This guide delves into the science behind optimal nutrition for fitness, covering topics such as macronutrient needs, meal timing, hydration, supplementation, and personalized nutrition plans.
From fueling your workouts and supporting muscle growth to optimizing recovery and preventing injury, nutrition plays a pivotal role in your fitness success. By understanding the principles of nutritional guidance for fitness, you can empower yourself to make informed choices that support your athletic endeavors and help you reach your full potential.
Understanding the Importance of Nutritional Guidance for Fitness
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in achieving fitness goals. It provides the fuel your body needs to perform, recover, and maintain overall well-being. By understanding the relationship between nutrition and fitness, you can optimize your training and reach your full potential.
The Role of Nutrition in Fitness
Nutrition is the foundation of fitness. It provides the building blocks for muscle growth, energy for workouts, and nutrients for recovery. By consuming a balanced diet that meets your individual needs, you can support your body’s ability to adapt to exercise and achieve optimal results.
Nutrition for Enhanced Performance
Proper nutrition is essential for maximizing athletic performance. Different nutrients play specific roles in enhancing various aspects of fitness.
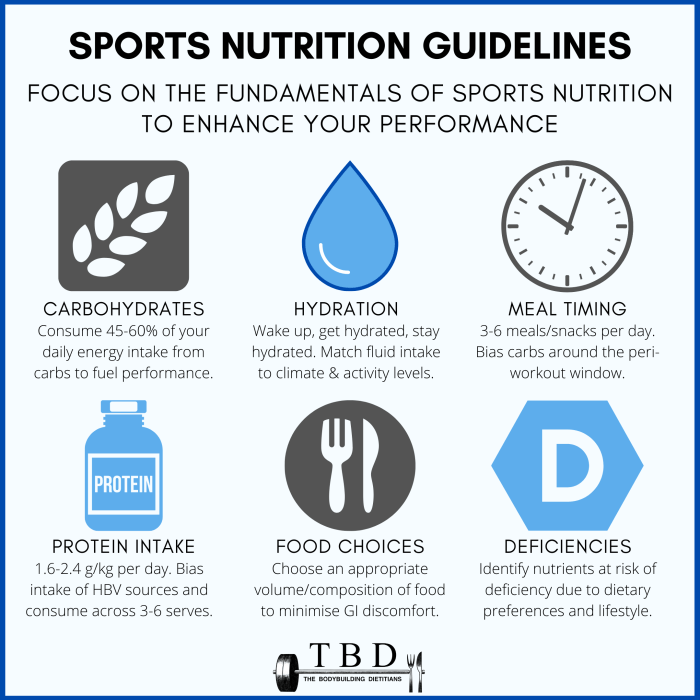
- Carbohydrates: Provide the primary source of energy for high-intensity workouts and endurance activities. Examples include whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins: Essential for muscle growth, repair, and recovery. Examples include lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, and tofu.
- Fats: Provide energy, support hormone production, and protect vital organs. Examples include healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Nutrition for Optimal Recovery
Recovery is just as important as training. Adequate nutrition helps your body repair muscle tissue, replenish energy stores, and prevent injuries.
- Protein: Consuming protein after exercise promotes muscle protein synthesis and repair.
- Carbohydrates: Replenish glycogen stores, which are depleted during intense workouts.
- Hydration: Water is crucial for recovery, as it helps regulate body temperature and transport nutrients.
Nutrition for Overall Well-being
Beyond performance and recovery, nutrition plays a vital role in overall health and well-being. A balanced diet can support a strong immune system, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and promote mental clarity.
- Fruits and vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which protect cells from damage and support overall health.
- Whole grains: Provide fiber, which aids digestion and promotes satiety.
- Lean protein: Contributes to a healthy heart and supports healthy blood sugar levels.
Macro and Micronutrient Needs for Fitness: Nutritional Guidance For Fitness
To achieve your fitness goals, it’s crucial to understand the role of macronutrients and micronutrients in fueling your workouts and supporting muscle recovery. Macronutrients are the building blocks of your diet, providing your body with energy and essential components for growth and repair.
Micronutrients, on the other hand, are vital for various bodily functions, including metabolism, immune function, and overall health.
Recommended Daily Macronutrient Intake for Different Fitness Levels
The recommended daily intake of macronutrients varies depending on your fitness level and goals. The table below provides a general guideline for different fitness levels:
| Fitness Level | Protein (g/kg body weight) | Carbohydrates (g/kg body weight) | Fat (g/kg body weight) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Recreational | 1.2-1.4 | 4-5 | 0.8-1.0 |
| Competitive | 1.6-2.0 | 6-7 | 0.8-1.0 |
| Strength Training | 1.6-2.2 | 4-5 | 0.8-1.0 |
| Endurance | 1.2-1.4 | 6-8 | 0.8-1.0 |
The Role of Protein, Carbohydrates, and Fats in Fueling Workouts and Supporting Muscle Recovery
Each macronutrient plays a crucial role in fueling your workouts and supporting muscle recovery:
Protein
Protein is essential for building and repairing muscle tissue. During exercise, muscle fibers break down, and protein provides the necessary amino acids to rebuild and strengthen them.
Adequate protein intake is crucial for optimal muscle growth and recovery, especially after intense workouts.
Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for your body, particularly during intense exercise. They are broken down into glucose, which your muscles use as fuel.
Consuming carbohydrates before and after workouts helps replenish glycogen stores and supports optimal performance.
Fats
Fats provide a concentrated source of energy and help with hormone production, cell function, and insulation. While not the primary fuel source for workouts, fats are important for overall health and recovery.
Healthy fats, like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are essential for optimal body function.
Essential Micronutrients for Fitness, Nutritional guidance for fitness
Micronutrients are essential for various bodily functions that support fitness:
Iron
Iron is crucial for red blood cell production, which carries oxygen to your muscles.
Iron deficiency can lead to fatigue and reduced exercise performance.
Calcium
Calcium is essential for strong bones and teeth, as well as muscle function.
Calcium deficiency can increase the risk of injuries and hinder muscle recovery.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D plays a vital role in calcium absorption and bone health.
Adequate vitamin D levels are crucial for overall health and bone strength, which are essential for fitness.
Magnesium
Magnesium is involved in over 300 bodily processes, including muscle function, energy production, and blood sugar control.
Magnesium deficiency can lead to muscle cramps, fatigue, and impaired performance.
Zinc
Zinc is essential for immune function, wound healing, and protein synthesis.
Zinc deficiency can impair immune function and hinder muscle recovery.
Meal Timing and Frequency for Optimal Performance

Meal timing, also known as nutritional timing, plays a crucial role in maximizing fitness gains. It involves strategically planning your meals and snacks around your training schedule to optimize performance, recovery, and overall health. By understanding the principles of meal timing, you can ensure your body receives the right nutrients at the right time to fuel your workouts, support muscle growth, and enhance your overall fitness journey.
Pre-Workout Nutrition
Pre-workout nutrition is essential for providing your body with the energy it needs to power through your workout. Consuming a balanced meal or snack about 1-2 hours before your training session can help improve your performance, endurance, and strength.
- Carbohydrates: Complex carbohydrates, such as oatmeal, brown rice, or whole-grain bread, provide sustained energy levels during your workout. They are broken down slowly, ensuring a steady supply of glucose to your muscles.
- Protein: A small amount of protein, such as a protein shake or Greek yogurt, can help preserve muscle mass and promote muscle recovery after your workout.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is crucial for optimal performance. Drink plenty of water in the hours leading up to your workout.
Post-Workout Nutrition
Post-workout nutrition is equally important for recovery and muscle growth. Consuming a meal or snack within 30-60 minutes after your workout can help replenish your energy stores, repair muscle tissue, and promote muscle protein synthesis.
- Carbohydrates: Replenishing glycogen stores is crucial for muscle recovery. Include carbohydrates like fruit, sweet potatoes, or whole-grain bread in your post-workout meal.
- Protein: Consuming protein after your workout is essential for muscle repair and growth. Aim for a protein source such as chicken breast, fish, or a protein shake.
- Hydration: It’s essential to rehydrate after your workout. Drink plenty of water or an electrolyte-rich beverage.
Daily Meal Planning
Planning your meals throughout the day is essential for consistent energy levels and optimal performance. Aim for a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods.
- Breakfast: Start your day with a balanced breakfast that includes carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. This will provide you with sustained energy throughout the morning.
- Lunch: Include a mix of carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats in your lunch to keep you energized and satisfied until dinner.
- Dinner: Ensure your dinner is a balanced meal that includes lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and plenty of vegetables.
- Snacks: Include healthy snacks throughout the day to prevent hunger pangs and maintain energy levels. Opt for options like fruits, vegetables, nuts, or yogurt.
Frequent, Smaller Meals vs. Fewer, Larger Meals
The frequency of your meals can impact your energy levels and performance. There are two main approaches: frequent, smaller meals or fewer, larger meals.
- Frequent, Smaller Meals: This approach involves consuming several smaller meals throughout the day, typically every 2-3 hours. It helps maintain stable blood sugar levels, provides a consistent energy supply, and reduces feelings of hunger.
- Fewer, Larger Meals: This approach involves consuming fewer, larger meals, typically 3-4 times a day. It can be more convenient for some individuals but may lead to greater fluctuations in blood sugar levels and potential feelings of fullness or sluggishness.
The optimal meal frequency depends on individual factors such as activity level, training schedule, and personal preferences. Experimenting with different approaches can help you determine what works best for your body and fitness goals.
Hydration and Electrolyte Balance for Fitness

Adequate hydration is crucial for optimal fitness performance and overall health. Water is essential for numerous bodily functions, including regulating body temperature, transporting nutrients, and removing waste products. During exercise, we lose fluids through sweat, and replenishing these fluids is essential for maintaining performance and preventing dehydration.
Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, play a critical role in hydration and muscle function.
Importance of Hydration for Fitness
Maintaining proper hydration is essential for fitness performance, particularly during and after workouts. Dehydration can lead to various negative effects, including:
- Reduced athletic performance: Dehydration can lead to decreased muscle strength, endurance, and overall performance.
- Increased risk of injury: Dehydration can impair coordination and balance, increasing the risk of falls and other injuries.
- Heat exhaustion and heat stroke: Dehydration can contribute to heat-related illnesses, which can be serious and even life-threatening.
- Muscle cramps: Dehydration can lead to electrolyte imbalances, which can cause muscle cramps.
Role of Electrolytes in Hydration and Cramps
Electrolytes are minerals that carry an electrical charge when dissolved in fluids, such as water. They play a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, muscle function, and nerve impulses. During exercise, electrolytes are lost through sweat. This loss of electrolytes can lead to imbalances, contributing to muscle cramps and fatigue.
- Sodium: Sodium is the primary electrolyte lost through sweat and is crucial for maintaining fluid balance.
- Potassium: Potassium is essential for muscle contraction and nerve function.
- Magnesium: Magnesium plays a role in muscle relaxation and energy production.
Optimal Hydration Strategies
Staying adequately hydrated is crucial for optimal fitness performance. Here are some strategies for achieving optimal hydration:
- Drink fluids regularly throughout the day, even when not thirsty.
- Drink water before, during, and after exercise.
- Choose fluids that contain electrolytes, especially during prolonged or intense exercise. Sports drinks can be beneficial in these situations.
- Avoid sugary drinks, as they can dehydrate you.
- Monitor your urine color. Light yellow urine indicates adequate hydration, while dark yellow urine suggests dehydration.
Supplementing for Fitness Goals

Fitness supplements can be a valuable tool for athletes and individuals looking to enhance their performance and achieve their fitness goals. While a balanced diet should always be the foundation of a healthy lifestyle, supplements can provide targeted support for specific needs.
However, it’s crucial to understand the potential benefits, risks, and responsible use of supplements before incorporating them into your routine.
Types of Fitness Supplements
Fitness supplements are available in a wide variety of forms, each designed to address specific aspects of athletic performance and recovery. Understanding the different types of supplements and their potential benefits can help you make informed choices.
- Protein Powders: Protein powders are a convenient way to increase protein intake, which is essential for muscle growth and repair. They are particularly beneficial for individuals who struggle to meet their protein needs through diet alone, such as athletes, vegetarians, or those with busy schedules.Whey protein, casein protein, and soy protein are some of the most common types of protein powders available.
- Creatine: Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in muscle tissue that plays a role in energy production. Supplementing with creatine can increase muscle mass, strength, and power output, making it popular among athletes in various sports.
- Multivitamins: Multivitamins are designed to supplement a balanced diet by providing a range of essential vitamins and minerals that may be lacking in some individuals. They can be beneficial for athletes who have increased nutrient requirements due to their training regimen.
- BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids): BCAAs are essential amino acids that are particularly important for muscle protein synthesis. Supplementing with BCAAs can help reduce muscle breakdown and improve recovery after exercise.
- Glutamine: Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid that plays a role in muscle recovery and immune function. Supplementing with glutamine may help reduce muscle soreness and improve recovery time.
- Pre-Workout Supplements: Pre-workout supplements are typically a blend of ingredients designed to enhance energy levels, focus, and endurance before exercise. They often contain caffeine, creatine, and other stimulants.
- Post-Workout Supplements: Post-workout supplements are designed to aid in muscle recovery and repair after exercise. They often contain protein, carbohydrates, and other nutrients that support muscle growth and replenishment of glycogen stores.
Comparing and Contrasting Supplements
Each type of supplement has its unique benefits and drawbacks. It’s essential to compare and contrast different supplements to determine which ones are most suitable for your individual needs and goals.
Protein Powders
Protein powders are a convenient and efficient way to increase protein intake, but they are not a substitute for a balanced diet.
- Whey Protein: Whey protein is a fast-digesting protein source derived from milk. It is absorbed quickly and is an excellent choice for post-workout recovery.
- Casein Protein: Casein protein is a slow-digesting protein source also derived from milk. It is absorbed gradually, providing a sustained release of amino acids.
- Soy Protein: Soy protein is a plant-based protein source that is a good alternative for individuals with dairy allergies or sensitivities.
Creatine
Creatine is a well-researched supplement that has been shown to improve muscle mass, strength, and power output.
- Benefits: Increased muscle mass, strength, and power output.
- Potential Risks: Some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort, such as bloating or diarrhea when taking creatine.
Multivitamins
Multivitamins can help fill in nutritional gaps and ensure that individuals are meeting their daily requirements for essential vitamins and minerals. However, they are not a substitute for a balanced diet.
- Benefits: Provides essential vitamins and minerals that may be lacking in some diets.
- Potential Risks: Taking high doses of certain vitamins and minerals can be harmful. It is important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines.
Responsible Supplement Use
While supplements can be beneficial, it’s crucial to use them responsibly to minimize potential risks and maximize their benefits.
- Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Before taking any supplements, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any underlying medical conditions or are taking medications.
- Choose Reputable Brands: Look for supplements from reputable brands that have been tested for quality and purity.
- Follow Dosage Guidelines: Always follow the recommended dosage guidelines on the supplement label. Exceeding the recommended dosage can lead to adverse effects.
- Be Aware of Potential Interactions: Some supplements can interact with medications or other supplements. It’s important to be aware of potential interactions and to talk to your healthcare professional if you have any concerns.
- Monitor for Side Effects: If you experience any adverse effects after taking a supplement, stop using it and consult with your healthcare professional.
Potential Risks of Supplements
While supplements can be beneficial, it’s important to be aware of the potential risks associated with their use.
- Side Effects: Some supplements can cause side effects, such as gastrointestinal discomfort, headaches, or insomnia.
- Interactions: Supplements can interact with medications or other supplements, leading to adverse effects.
- Contamination: Some supplements may be contaminated with harmful substances, such as heavy metals or bacteria.
- Misleading Marketing: Some supplement manufacturers make misleading claims about the effectiveness of their products. It’s important to be a critical consumer and to research supplements thoroughly before using them.
Nutrition for Specific Fitness Activities

Proper nutrition plays a crucial role in supporting different fitness goals and optimizing performance. The type and amount of food you consume can significantly impact your energy levels, recovery, and overall progress. Understanding the dietary needs for specific fitness activities is essential for maximizing your results and preventing potential deficiencies.
Dietary Needs for Different Fitness Activities
This table illustrates the dietary needs for different fitness activities, including endurance training, strength training, and weight loss:
| Fitness Activity | Macronutrient Needs | Specific Food Choices |
|---|---|---|
| Endurance Training | Higher carbohydrate intake for sustained energy, moderate protein for muscle repair, and adequate fat for hormone production. | Whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean protein sources (chicken, fish), healthy fats (avocados, nuts). |
| Strength Training | Higher protein intake for muscle growth and repair, adequate carbohydrates for energy, and healthy fats for hormone production. | Lean protein sources (chicken, fish, tofu), complex carbohydrates (brown rice, quinoa), healthy fats (olive oil, nuts). |
| Weight Loss | Calorie deficit with balanced macronutrients, focusing on nutrient-dense foods for satiety and optimal health. | Fruits, vegetables, lean protein sources, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products. |
Food Choices for Optimal Performance
Specific food choices can support optimal performance in different fitness activities. For endurance training, focusing on carbohydrates and electrolytes is crucial. Foods like bananas, potatoes, and sports drinks can replenish glycogen stores and prevent dehydration. For strength training, consuming protein-rich foods after workouts is essential for muscle recovery and growth.
Examples include chicken breast, Greek yogurt, and protein shakes. For weight loss, choosing nutrient-dense foods with lower calorie content is important. Fruits, vegetables, and lean protein sources can provide satiety and support a calorie deficit.
Sample Meal Plans
Here are examples of sample meal plans tailored to different fitness goals:
Endurance Training Meal Plan
Breakfast
Oatmeal with berries and nuts
Lunch
Grilled chicken salad with quinoa and avocado
Dinner
Salmon with roasted vegetables and brown rice
Snacks
Fruit, yogurt, trail mix
Strength Training Meal Plan
Breakfast
Scrambled eggs with whole-wheat toast and spinach
Lunch
Tuna salad sandwich on whole-wheat bread
Dinner
Chicken breast with sweet potatoes and broccoli
Snacks
Protein shake, Greek yogurt
Weight Loss Meal Plan
Breakfast
Smoothie with fruit, spinach, and protein powder
Lunch
Salad with grilled chicken and vegetables
Dinner
Lentil soup with whole-wheat bread
Snacks
Apple slices with peanut butter, almonds
Addressing Common Nutritional Challenges for Fitness
Maintaining a healthy diet while pursuing fitness goals can be challenging. Many individuals face obstacles such as calorie counting, portion control, and avoiding processed foods. This section explores these common challenges and provides practical strategies to overcome them.
Calorie Counting and Portion Control
Calorie counting and portion control are essential for achieving fitness goals. Understanding calorie needs and adjusting portions accordingly can help individuals create a sustainable calorie deficit or surplus.
- Use a calorie tracking app: These apps can help individuals monitor their calorie intake and identify areas for improvement. Popular options include MyFitnessPal, Lose It!, and Cronometer.
- Practice mindful eating: Paying attention to hunger cues and eating slowly can help individuals avoid overeating.
- Use smaller plates and bowls: This creates the illusion of a larger portion, making individuals feel more satisfied with less food.
- Read food labels carefully: Pay attention to serving sizes and calories per serving.
Avoiding Processed Foods
Processed foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, sugar, and sodium, which can hinder fitness progress.
- Focus on whole, unprocessed foods: Choose fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains over processed snacks and meals.
- Cook more meals at home: This allows individuals to control ingredients and portion sizes.
- Read ingredient lists: Avoid foods with long lists of unfamiliar ingredients or added sugars, artificial flavors, and preservatives.
- Choose healthier alternatives: Opt for whole-wheat bread over white bread, grilled chicken over fried chicken, and unsweetened yogurt over flavored yogurt.
Healthy Snack Options and Meal Replacements
Having healthy snacks and meal replacements on hand can help individuals avoid unhealthy cravings and stay on track with their fitness goals.
- Healthy snacks: Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, Greek yogurt, hard-boiled eggs, and protein bars.
- Meal replacements: Protein shakes, smoothies, and meal replacement bars.
Wrap-Up
As you embark on your fitness journey, remember that nutritional guidance is an ongoing process. What works for one person may not work for another, and your needs may evolve as your fitness goals change. By embracing the principles articulated in this guide and seeking personalized advice from a registered dietitian or nutritionist, you can establish a sustainable nutritional foundation that supports your fitness success and promotes a healthy, active lifestyle.
Comments are closed.