Sleeps Importance for Overall Wellness

The importance of sleep for wellness sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. Sleep, often viewed as a passive state, is a vital biological process that profoundly impacts our physical, mental, and emotional well-being.
It’s a time when our bodies and minds can rejuvenate, repair, and prepare for the challenges of the day ahead. Throughout this exploration, we’ll delve into the science of sleep, uncovering the intricate mechanisms that orchestrate its restorative power. We’ll examine the profound connection between sleep and our physical health, exploring how it strengthens our immune system, regulates hormones, and safeguards our cardiovascular health.
Furthermore, we’ll unravel the intricate relationship between sleep and mental well-being, uncovering its role in mood regulation, cognitive function, and emotional resilience. By understanding the science behind sleep and its impact on our lives, we can cultivate healthier sleep habits and unlock the transformative power of rest.
This journey into the world of sleep will equip you with valuable knowledge and practical strategies to prioritize sleep and optimize your overall well-being. We’ll navigate the complexities of sleep disorders, providing insights into their causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options.
Ultimately, this exploration will empower you to make informed decisions about your sleep habits, fostering a healthier and more fulfilling life.
The Science of Sleep
Sleep is an essential biological process that plays a vital role in maintaining our physical and mental well-being. During sleep, our bodies and minds engage in a complex symphony of activities that are crucial for our overall health and performance.
Understanding the science of sleep can empower us to prioritize it and reap its numerous benefits.
The Stages of Sleep
Sleep is not a monolithic state but rather a journey through distinct stages, each with its unique functions. These stages are characterized by different brain wave patterns, physiological changes, and levels of consciousness.
- Stage 1: NREM 1 (Light Sleep): This stage is a transition between wakefulness and sleep, characterized by a slowing of heart rate and muscle activity. It is the stage where we may experience hypnic jerks, those sudden muscle twitches that can jolt us awake.
- Stage 2: NREM 2 (Light Sleep): As we progress into stage 2, our brain waves slow further, and our body temperature drops. This stage is characterized by brief bursts of brain activity called sleep spindles and K-complexes, which help suppress sensory input and maintain sleep.
- Stage 3: NREM 3 (Deep Sleep): This stage is the deepest stage of sleep, where our brain waves become very slow and our muscles relax completely. It is crucial for physical restoration, muscle growth, and hormone production.
- Stage 4: REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep: This stage is characterized by rapid eye movements, increased brain activity, and muscle paralysis. It is associated with dreaming and is crucial for memory consolidation, emotional processing, and creativity.
Biological Processes During Sleep
Sleep is not merely a period of inactivity but rather a time of intense biological activity that supports our physical and mental well-being.
- Cellular Repair and Growth: During sleep, our cells engage in repair and regeneration processes, rebuilding tissues and replenishing energy stores. This is particularly important for muscle growth and repair, as well as the restoration of organs and tissues.
- Hormone Regulation: Sleep plays a crucial role in regulating the production and release of hormones, including growth hormone, cortisol, and melatonin. Growth hormone is essential for growth and development, while cortisol helps regulate stress response, and melatonin promotes sleep and circadian rhythm.
- Immune System Strengthening: Sleep is crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. During sleep, our body produces cytokines, which are proteins that help fight infections and inflammation.
- Memory Consolidation: Sleep is essential for consolidating memories and transferring information from short-term to long-term memory. During REM sleep, the brain processes and strengthens memories formed during the day, enhancing learning and recall.
- Emotional Regulation: Sleep plays a critical role in emotional regulation. During sleep, the brain processes and integrates emotional experiences, helping us cope with stress and maintain emotional stability.
Impact of Sleep Deprivation, Importance of sleep for wellness
Chronic sleep deprivation can have significant and detrimental effects on our physical and mental health.
- Cognitive Impairment: Sleep deprivation can impair cognitive function, leading to reduced attention span, difficulty concentrating, and impaired decision-making. It can also affect memory consolidation and learning.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Research has shown a strong link between sleep deprivation and an increased risk of chronic diseases such as obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and stroke.
- Mental Health Issues: Sleep deprivation can exacerbate existing mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, and increase the risk of developing new ones.
- Weakened Immune System: Chronic sleep deprivation can weaken the immune system, making us more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Sleep deprivation can impair alertness and reaction time, increasing the risk of accidents, especially while driving or operating machinery.
Sleep and Physical Health

Sleep is not merely a period of rest; it is a crucial pillar of overall wellness, profoundly impacting our physical health. During sleep, our bodies work tirelessly to repair and rejuvenate, ensuring optimal functioning for the day ahead.
Sleep and the Immune System
Sleep plays a vital role in bolstering our immune defenses, acting as a shield against infections. While we sleep, our bodies produce proteins called cytokines, which are essential for fighting off infections and inflammation. Studies have shown that chronic sleep deprivation can suppress the production of these crucial immune cells, making us more susceptible to illness.
For instance, research has linked insufficient sleep to an increased risk of catching a cold.
Sleep and Hormone Regulation
Sleep profoundly influences the intricate dance of hormones in our bodies. During sleep, our bodies release growth hormones, which are essential for tissue repair, growth, and development. Sleep deprivation can disrupt this delicate balance, leading to a decline in growth hormone production.
Additionally, sleep plays a crucial role in regulating cortisol levels, the stress hormone. When we sleep adequately, our cortisol levels naturally decline, promoting relaxation and a sense of well-being. However, sleep deprivation can lead to an elevation in cortisol levels, contributing to stress, anxiety, and even weight gain.
Sleep and Cardiovascular Health
The impact of sleep on cardiovascular health is undeniable. Sufficient sleep is a powerful ally in maintaining a healthy heart. Studies have shown that individuals who get enough sleep have a lower risk of developing high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
On the other hand, chronic sleep deprivation can lead to an increase in blood pressure, heart rate, and inflammation, all of which can contribute to cardiovascular disease. For example, a study published in the journal “Sleep” found that people who slept less than six hours per night had a 20% higher risk of developing heart disease than those who slept seven or more hours.
Sleep and Mental Health: Importance Of Sleep For Wellness

Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining our mental well-being. A consistent sleep schedule and sufficient sleep duration are essential for optimal cognitive function, emotional regulation, and overall mental health.
The Connection Between Sleep and Mood Disorders
Sleep disturbances are commonly associated with mood disorders, such as depression and anxiety. A lack of sleep can exacerbate symptoms of these disorders, while consistent sleep deprivation can even trigger the onset of mood disorders in some individuals.
- Depression: Studies have shown a strong correlation between sleep disturbances and depression. People with depression often experience difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up feeling refreshed. Furthermore, sleep deprivation can lead to a decline in mood, increased fatigue, and difficulty concentrating, which can worsen depressive symptoms.
- Anxiety: Similarly, sleep disturbances are prevalent in individuals with anxiety disorders. Anxiety can interfere with sleep, causing insomnia, nightmares, and restless sleep. In turn, sleep deprivation can amplify anxiety symptoms, leading to increased worry, irritability, and difficulty managing stress.
The Role of Sleep in Cognitive Function
Sleep is essential for cognitive function, particularly for memory consolidation and attention. During sleep, the brain processes and consolidates information acquired during the day, transferring memories from short-term to long-term storage. Sleep deprivation can significantly impair these processes, leading to difficulties with learning, memory, and attention.
- Memory Consolidation: During sleep, the brain replays and strengthens memories, enhancing their retention. Sleep deprivation can disrupt this process, leading to impaired memory consolidation and difficulty recalling information.
- Attention: Adequate sleep is crucial for maintaining focus and attention. Sleep deprivation can lead to decreased alertness, difficulty concentrating, and impaired decision-making abilities.
The Impact of Sleep on Emotional Regulation and Stress Management
Sleep plays a vital role in emotional regulation and stress management. When we are well-rested, we are better equipped to cope with stress, regulate our emotions, and maintain a positive outlook. Conversely, sleep deprivation can lead to increased emotional reactivity, difficulty managing stress, and a heightened risk of experiencing negative emotions.
- Emotional Regulation: Sleep deprivation can make it harder to control emotions, leading to increased irritability, mood swings, and difficulty managing anger.
- Stress Management: Sleep deprivation can increase levels of the stress hormone cortisol, making it more difficult to cope with stress. Furthermore, a lack of sleep can impair our ability to think clearly and make rational decisions, further contributing to stress.
Sleep Habits and Lifestyle Factors

Your sleep habits and lifestyle choices significantly impact your sleep quality. While genetics play a role, adopting healthy sleep habits and making mindful lifestyle changes can significantly improve your sleep and overall well-being.
Healthy Sleep Habits
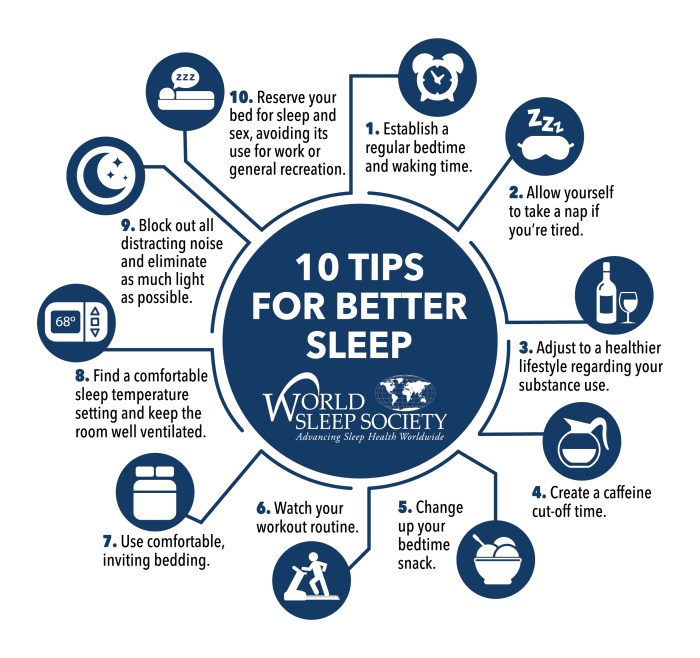
Establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and optimizing your sleep environment are crucial for restful sleep.
- Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends, to regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle (circadian rhythm).
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Wind down an hour or two before bed by engaging in calming activities like taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to soothing music. Avoid screen time, as the blue light emitted from electronic devices can interfere with melatonin production, a hormone that regulates sleep.
- Optimize Your Sleep Environment: Make sure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. A comfortable temperature of around 65 degrees Fahrenheit (18 degrees Celsius) is ideal for sleep. Use blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out light, earplugs to minimize noise, and a white noise machine to create a soothing atmosphere.
- Limit Daytime Naps: Short naps can be beneficial, but long or frequent naps can disrupt your nighttime sleep. If you do nap, keep it short (20-30 minutes) and avoid napping late in the afternoon.
- Get Regular Exercise: Physical activity can promote better sleep, but avoid exercising too close to bedtime.
- Avoid Heavy Meals Before Bed: A heavy meal can disrupt sleep. Eat dinner a few hours before bedtime and avoid sugary snacks or caffeine before bed.
Influence of Caffeine, Alcohol, and Nicotine
Caffeine, alcohol, and nicotine can disrupt your sleep cycle and negatively impact your sleep quality.
- Caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can interfere with sleep, especially when consumed late in the day. The effects of caffeine can last for several hours, so avoid it in the afternoon and evening.
- Alcohol: While alcohol may make you feel sleepy initially, it disrupts your sleep cycle in the long run. Alcohol can lead to lighter sleep, frequent awakenings, and nightmares.
- Nicotine: Nicotine is a stimulant that can interfere with sleep, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep.
Creating a Conducive Sleep Environment
A comfortable and conducive sleep environment is crucial for restful sleep.
- Temperature: A cool bedroom temperature, around 65 degrees Fahrenheit (18 degrees Celsius), is ideal for sleep. A comfortable temperature helps regulate your body temperature and promotes deeper sleep.
- Lighting: Darkness is essential for sleep. Dim the lights in your home an hour or two before bed and use blackout curtains or an eye mask to block out any remaining light.
- Noise: Noise can disrupt sleep. Use earplugs or a white noise machine to minimize distracting sounds.
- Bed and Bedding: A comfortable bed and bedding are essential for restful sleep. Choose a mattress that provides adequate support and a pillow that supports your head and neck. Use breathable sheets and blankets that are not too heavy or too light.
Sleep Disorders and Treatments

Sleep disorders are common and can significantly impact overall health and well-being. Understanding the different types of sleep disorders, their causes, and available treatments is crucial for managing these conditions effectively.
Common Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders encompass a range of conditions that disrupt normal sleep patterns and can lead to daytime sleepiness, difficulty concentrating, and other health problems. Here are some of the most prevalent sleep disorders:
- Insomnia: Insomnia is characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or both. It can be short-term (acute) or long-term (chronic). Common causes include stress, anxiety, depression, and certain medical conditions.
- Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea is a disorder where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. There are two main types: obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), where the airway is blocked, and central sleep apnea (CSA), where the brain fails to send signals to the muscles that control breathing.
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that causes excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden attacks of sleep, and other sleep-related symptoms. It is caused by a deficiency in the brain chemical hypocretin, which regulates sleep-wake cycles.
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS): RLS is a neurological disorder that causes an irresistible urge to move the legs, often accompanied by unpleasant sensations in the legs. Symptoms are usually worse at night and can disrupt sleep.
- Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders: These disorders involve misalignment between the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle and the desired or required sleep schedule. Examples include jet lag, shift work sleep disorder, and delayed sleep-wake phase disorder.
Treatment Options for Sleep Disorders
Treatment for sleep disorders often involves a combination of approaches tailored to the specific condition and individual needs. Here are some common treatment options:
Behavioral Therapy
Behavioral therapy focuses on modifying sleep habits and behaviors to improve sleep quality. Some common techniques include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I): CBT-I helps individuals identify and change negative thoughts and behaviors related to sleep. It involves techniques like relaxation training, sleep restriction, and stimulus control.
- Sleep Hygiene Education: This involves educating patients on healthy sleep habits, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed.
Medication
Medication can help manage certain sleep disorders, but it is usually used in conjunction with other therapies. Some common medications used for sleep disorders include:
- Hypnotics: These medications promote sleep and can be helpful for short-term insomnia. However, long-term use can lead to dependence and tolerance.
- Sedatives: Sedatives can be used to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation, which may improve sleep quality.
- Stimulants: In cases of excessive daytime sleepiness, such as narcolepsy, stimulants can help improve alertness and reduce sleepiness.
Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes can play a significant role in improving sleep quality. Some key changes include:
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality, but avoid exercising too close to bedtime.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote better sleep. Avoid heavy meals and sugary snacks before bed.
- Limit Caffeine and Alcohol: Caffeine and alcohol can interfere with sleep, so limit consumption, especially in the hours leading up to bedtime.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as taking a warm bath, reading a book, or listening to relaxing music.
- Maintain a Comfortable Sleep Environment: Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Use a comfortable mattress, pillows, and bedding.
Resources and Support Groups
If you are struggling with sleep issues, there are resources and support groups available to help. Here are some organizations that can provide information, support, and treatment options:
- National Sleep Foundation (NSF): The NSF is a non-profit organization that provides information and resources on sleep health, including sleep disorders and treatments. Visit their website at [website address].
- American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM): The AASM is a professional organization that promotes sleep medicine research and education. They offer resources for patients and healthcare providers. Visit their website at [website address].
- Sleep Foundation: The Sleep Foundation is an independent organization that provides information and resources on sleep health, including sleep disorders, treatments, and sleep tips. Visit their website at [website address].
- Local Sleep Clinics and Centers: Many communities have sleep clinics and centers that offer diagnosis, treatment, and support for sleep disorders. Contact your local healthcare provider or search online for sleep clinics in your area.
Ending Remarks

Sleep, once considered a mere luxury, is now recognized as a fundamental pillar of our well-being. By understanding the science behind sleep and its impact on our physical, mental, and emotional health, we can prioritize rest and unlock its transformative power.
Through conscious efforts to cultivate healthy sleep habits, we can create a foundation for a more vibrant, resilient, and fulfilling life. Let us embrace the power of sleep, recognizing it as an essential ingredient in our journey toward optimal health and happiness.
Comments are closed.