Deep Breathing Exercises for Anxiety: A Guide to Calm
Deep breathing exercises for anxiety offer a powerful tool for managing stress and promoting emotional well-being. Anxiety is a common human experience, often manifesting as racing thoughts, physical tension, and feelings of overwhelm. Deep breathing techniques work by directly influencing the nervous system, calming the body’s fight-or-flight response, and promoting a sense of relaxation.
This article will explore various deep breathing exercises, their benefits, and how to incorporate them into daily life.
By learning and practicing these techniques, you can empower yourself to navigate anxiety more effectively and experience a greater sense of peace and tranquility. Whether you’re dealing with everyday stress or managing a specific anxiety disorder, deep breathing exercises can be a valuable tool for improving your overall mental health and well-being.
Understanding Anxiety and Deep Breathing

Anxiety is a natural human response to stress, but when it becomes excessive or persistent, it can significantly impact our well-being. Deep breathing exercises are a powerful tool for managing anxiety, as they can help calm the nervous system and promote relaxation.
Physiological Effects of Anxiety
Anxiety triggers a cascade of physiological changes in the body, preparing us for a perceived threat, even if the threat is not real. These changes can include:
- Increased heart rate: The heart beats faster to deliver more oxygen to the muscles, preparing for fight or flight.
- Rapid breathing: The body takes in more oxygen to fuel the muscles.
- Muscle tension: Muscles tense up to prepare for action.
- Sweating: The body releases sweat to cool down the muscles.
- Dry mouth: Saliva production decreases as the body redirects resources to more essential functions.
- Digestive issues: Blood flow is diverted from the digestive system to the muscles, potentially causing nausea or stomach upset.
- Difficulty concentrating: The brain focuses on the perceived threat, making it difficult to concentrate on other tasks.
How Deep Breathing Counters Anxiety
Deep breathing exercises can help counteract the physiological effects of anxiety by:
- Slowing the heart rate: Deep, slow breaths send signals to the nervous system to calm down, leading to a slower heart rate.
- Regulating breathing: Deep breathing helps regulate the rhythm of breathing, reducing the rapid breathing associated with anxiety.
- Reducing muscle tension: Deep breaths help relax the muscles, releasing tension throughout the body.
- Promoting relaxation: Deep breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, responsible for rest and relaxation, counteracting the fight-or-flight response triggered by anxiety.
Examples of Anxiety in Daily Life
Anxiety can manifest in various ways, impacting daily life in numerous aspects:
- Social situations: Feeling nervous or anxious in social gatherings, public speaking, or meeting new people.
- Work: Feeling overwhelmed with work responsibilities, deadlines, or difficult tasks.
- Relationships: Experiencing anxiety in close relationships, such as with family, friends, or partners.
- Health concerns: Worrying excessively about health issues or experiencing anxiety related to medical procedures.
- Financial stress: Feeling anxious about finances, debt, or job security.
- Travel: Feeling anxious about traveling, such as flying or driving long distances.
Types of Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep Breathing Exercises For Anxiety
Deep breathing exercises are a powerful tool for managing anxiety. They work by slowing down your heart rate, lowering your blood pressure, and promoting relaxation. These exercises can be practiced anywhere, anytime, making them a convenient and accessible way to manage stress.
Different Deep Breathing Techniques
There are many different deep breathing techniques, each with its own set of benefits. Here are some of the most popular and effective techniques:
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: This technique focuses on using your diaphragm, the large muscle below your lungs, to breathe deeply. It is considered one of the most effective techniques for anxiety management.
- Lie down on your back with your knees bent and your feet flat on the floor.
- Place one hand on your chest and the other on your stomach, just below your ribs.
- Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose, allowing your stomach to rise as you breathe in. Your chest should remain relatively still.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth, allowing your stomach to fall as you breathe out.
- Repeat this process for 5-10 minutes, focusing on the sensation of your breath.
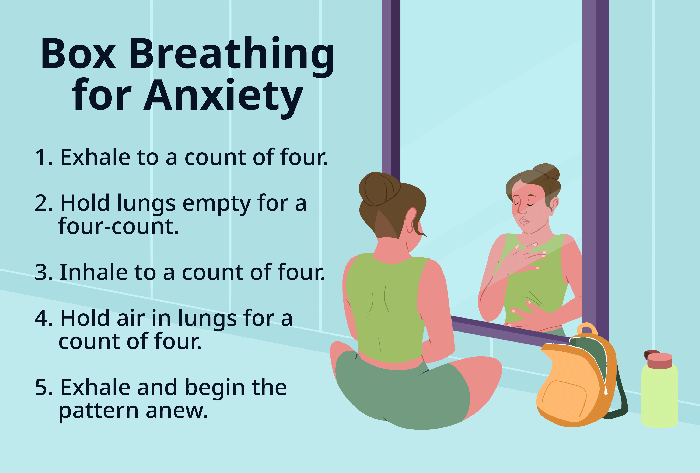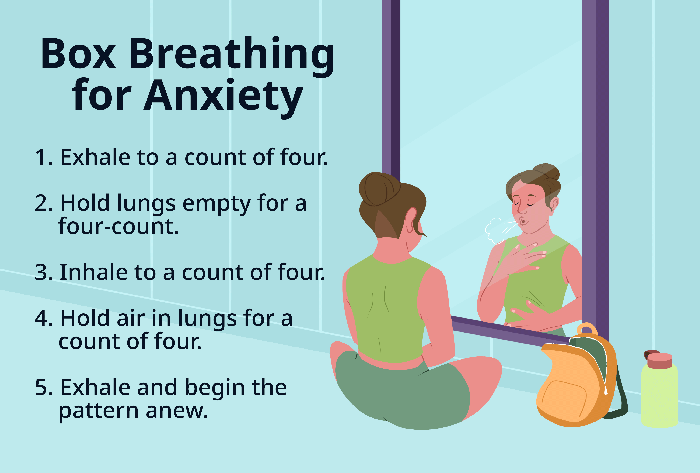
- Box Breathing: This technique is simple and effective for calming the mind and body. It involves breathing in a pattern that resembles a square.
- Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose for a count of four.
- Hold your breath for a count of four.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of four.
- Hold your breath for a count of four.
- Repeat this process for 5-10 minutes, focusing on the sensation of your breath.
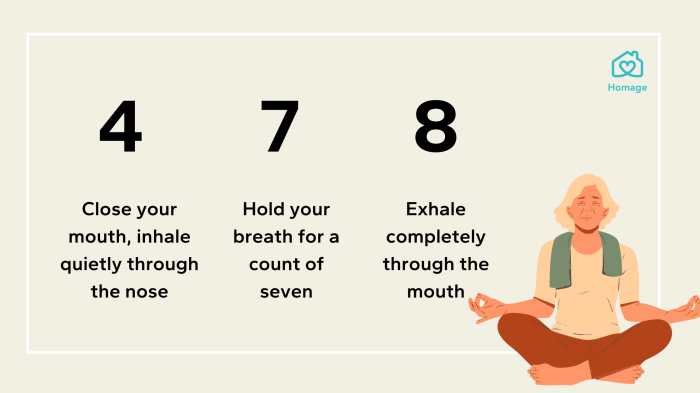
- 4-7-8 Breathing: This technique is designed to promote relaxation and sleep. It involves a specific breathing pattern that can help calm the nervous system.
- Close your eyes and gently exhale all the air from your lungs.
- Inhale deeply through your nose for a count of four.
- Hold your breath for a count of seven.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of eight.
- Repeat this process 4-5 times, focusing on the sensation of your breath.
- Alternate Nostril Breathing: This technique involves breathing alternately through each nostril, which is believed to help balance the energy in the body.
- Sit comfortably with your spine straight.
- Close your right nostril with your right thumb and inhale deeply through your left nostril.
- Close your left nostril with your right ring finger and exhale through your right nostril.
- Inhale through your right nostril.
- Close your right nostril and exhale through your left nostril.
- Repeat this process for 5-10 minutes, focusing on the sensation of your breath.
Breathing Techniques for Different Anxiety Levels
The effectiveness of different breathing techniques can vary depending on the individual and the level of anxiety. For mild anxiety, simple techniques like diaphragmatic breathing or box breathing may be sufficient. For moderate to severe anxiety, techniques like 4-7-8 breathing or alternate nostril breathing may be more helpful.
It’s important to experiment with different techniques and find what works best for you.
Benefits of Deep Breathing for Anxiety
Deep breathing exercises have become a popular technique for managing anxiety, and for good reason. The science behind deep breathing reveals its effectiveness in calming the nervous system and reducing stress. This section explores the benefits of deep breathing, providing evidence-based insights into its impact on anxiety.
Scientific Evidence Supporting Deep Breathing for Anxiety
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of deep breathing in reducing anxiety symptoms. One study published in the Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine found that deep breathing exercises significantly reduced anxiety levels in individuals with generalized anxiety disorder.
Another study published in the journal “Stress and Health” showed that deep breathing was effective in reducing anxiety symptoms in people experiencing public speaking anxiety. These studies, along with others, provide strong scientific evidence supporting the benefits of deep breathing for anxiety.
Deep Breathing Reduces Stress Hormones and deep breathing exercises for anxiety.
Deep breathing exercises have been shown to decrease the production of stress hormones like cortisol. When we experience anxiety, our bodies release stress hormones, leading to a cascade of physiological changes that contribute to feelings of unease and tension.
Deep breathing helps regulate the nervous system, promoting relaxation and reducing the release of stress hormones. By calming the body’s stress response, deep breathing can help alleviate anxiety symptoms.
Anecdotal Evidence of Deep Breathing for Anxiety
Beyond scientific evidence, numerous individuals have shared their personal experiences with deep breathing and its impact on their anxiety. Many report feeling calmer and more grounded after practicing deep breathing exercises. Some have found that deep breathing helps them manage anxiety in stressful situations, such as public speaking or social gatherings.
These anecdotal experiences highlight the potential of deep breathing as a self-management tool for anxiety.
Incorporating Deep Breathing into Daily Life

Deep breathing exercises are a powerful tool for managing anxiety, but their true potential lies in their integration into your daily routine. By making deep breathing a regular practice, you can build resilience and reduce the likelihood of anxiety taking hold.
Designing a Daily Routine
A consistent routine helps establish deep breathing as a habit. Here’s a sample daily schedule you can adapt to your needs:
- Morning: Begin your day with a few minutes of deep breathing exercises. This can help calm your mind and set a positive tone for the day. Try box breathing or alternate nostril breathing.
- Mid-day: Incorporate deep breathing during your lunch break or whenever you feel overwhelmed. A quick 5-minute session can help you refocus and manage stress.
- Evening: Before bed, practice deep breathing to unwind and promote relaxation. This can help improve sleep quality and reduce nighttime anxiety.
Deep Breathing in Various Situations
Deep breathing can be practiced anywhere, anytime. Here are some tips for incorporating it into different situations:
- Work: Take short breaks throughout the day to engage in deep breathing exercises. This can help manage stress and improve focus. For instance, during a particularly demanding task, take a 30-second pause to practice diaphragmatic breathing.
- Social Gatherings: If you feel anxious in social situations, use deep breathing as a coping mechanism. Discreetly practice deep breaths before entering a room or during a conversation to calm your nerves. For example, while waiting in line at a coffee shop, take a few deep breaths to manage your anxiety.
- Public Transportation: Utilize the time spent commuting to practice deep breathing exercises. This can help you relax and de-stress before arriving at your destination. Imagine yourself taking a calming walk in nature while practicing deep breathing on the bus or train.
Integrating Deep Breathing into Mindfulness Practices
Deep breathing is a core element of mindfulness practices. Here’s how to integrate it:
- Mindful Meditation: Deep breathing is often the foundation of mindful meditation. Focus on your breath as you inhale and exhale, observing the sensations without judgment. This helps cultivate present-moment awareness and reduce mental chatter.
- Body Scan Meditation: Combine deep breathing with a body scan meditation. As you breathe deeply, pay attention to different parts of your body, noticing any sensations without judgment. This can help you become more aware of your physical state and alleviate tension.
- Walking Meditation: While walking, synchronize your breath with your steps. This helps you stay present and connect with your body. As you inhale, take a step forward, and as you exhale, take another step. This mindful movement can help reduce anxiety and improve focus.
Deep Breathing for Specific Anxiety Disorders

Deep breathing exercises can be a valuable tool for managing various anxiety disorders. By regulating your breath, you can calm your nervous system and reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety, such as rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, and muscle tension.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Deep breathing can be particularly helpful for individuals with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), a condition characterized by persistent and excessive worry about various aspects of life. Deep, slow breaths can help to activate the parasympathetic nervous system, which promotes relaxation and reduces the “fight-or-flight” response triggered by anxiety.
This can help individuals with GAD to manage their worries and reduce feelings of tension.
Panic Attacks
Deep breathing is a common technique used to manage panic attacks. Panic attacks involve sudden, intense fear or discomfort that is often accompanied by physical symptoms like chest pain, dizziness, and a feeling of impending doom. By focusing on deep, slow breaths, individuals can help to slow their heart rate, reduce hyperventilation, and regain a sense of control during a panic attack.
Other Anxiety Disorders
Deep breathing can also be beneficial for other anxiety disorders, including:
- Social Anxiety Disorder: Deep breathing can help to reduce physical symptoms of anxiety, such as blushing and trembling, which can be particularly helpful in social situations.
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Deep breathing can be used to manage flashbacks and nightmares, which are common symptoms of PTSD.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): Deep breathing can help to reduce anxiety and intrusive thoughts associated with OCD.
Deep Breathing Techniques for Visualization and Relaxation
It can be combined with visualization and relaxation exercises to enhance their effectiveness in managing anxiety. These techniques can help calm the mind, reduce physical tension, and promote a sense of well-being.
Visualization Exercise with Deep Breathing
Visualization exercises involve creating mental images to evoke specific emotions or experiences. Combining deep breathing with visualization can create a more immersive and impactful experience. Here’s a simple visualization exercise:
- Find a quiet and comfortable place where you can sit or lie down.
- Close your eyes and take a few deep breaths, inhaling slowly through your nose and exhaling slowly through your mouth.
- Imagine yourself in a peaceful and serene environment, such as a beach, a forest, or a mountaintop.
- Focus on the details of this environment, such as the sound of waves crashing on the shore, the rustling of leaves in the wind, or the feeling of soft sand beneath your feet.
- As you breathe in, visualize yourself feeling calm and relaxed. As you breathe out, visualize any stress or tension leaving your body.
- Continue this visualization for 5-10 minutes, allowing yourself to fully immerse in the experience.
Guided Relaxation Technique with Deep Breathing
Guided relaxation techniques involve following a series of instructions that lead to a state of deep relaxation. Deep breathing is often incorporated into these techniques to help calm the mind and body. Here’s a simple guided relaxation technique:
- Lie down comfortably in a quiet place, with your eyes closed.
- Take a few deep breaths, inhaling slowly through your nose and exhaling slowly through your mouth.
- Focus on your breath, noticing the sensation of air entering and leaving your body.
- Start to scan your body, beginning with your toes and moving up to your head. As you focus on each body part, notice any tension or tightness and imagine it melting away with each exhale.
- Continue this process until you have scanned your entire body, feeling a sense of relaxation throughout.
- Stay in this relaxed state for a few minutes, enjoying the feeling of peace and calm.
Deep Breathing for Enhanced Relaxation and Mental Clarity
Deep breathing techniques can enhance relaxation and mental clarity by activating the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the body’s “rest and digest” response. This response helps to slow down the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and reduce muscle tension.
When the body is in a relaxed state, the mind is better able to focus and think clearly.
Deep breathing techniques can help to regulate the body’s stress response, promoting a sense of calm and tranquility.
Combining Deep Breathing with Other Techniques

Deep breathing exercises can be effectively combined with other techniques to enhance their overall impact on anxiety management. By integrating deep breathing with practices like meditation, yoga, or aromatherapy, individuals can create a holistic approach to reducing anxiety and promoting well-being.
Deep Breathing and Meditation
Meditation involves focusing the mind on a single point, such as the breath, to achieve a state of mental clarity and calmness. Combining deep breathing with meditation can amplify the benefits of both practices. When deep breathing is incorporated into meditation, it helps to regulate the breath, bringing the body into a state of relaxation.
This can enhance the meditative experience by calming the mind and reducing distracting thoughts.
“Deep breathing techniques can be used to calm the mind and body during meditation, allowing for a deeper state of relaxation and mindfulness.”
Deep Breathing and Yoga
Yoga is a practice that combines physical postures, breathing exercises, and meditation. Deep breathing plays a crucial role in yoga, as it helps to enhance flexibility, improve circulation, and promote relaxation. By integrating deep breathing techniques into yoga postures, individuals can deepen their stretches, increase their awareness of their breath, and cultivate a sense of mindfulness.
“The combination of deep breathing and yoga postures can create a synergistic effect, enhancing both physical and mental well-being.”
Deep Breathing and Aromatherapy
Aromatherapy involves using essential oils to promote physical and emotional well-being. Certain essential oils, such as lavender, chamomile, and bergamot, have calming properties that can reduce anxiety. When combined with deep breathing exercises, aromatherapy can create a more immersive and relaxing experience.
The inhalation of essential oils can enhance the calming effects of deep breathing, promoting a sense of peace and tranquility.
“Aromatherapy, when combined with deep breathing, can create a multi-sensory experience that enhances relaxation and reduces anxiety.”
Summary
Deep breathing exercises provide a natural and accessible path towards managing anxiety. By understanding the science behind these techniques and incorporating them into your daily routine, you can cultivate a sense of inner calm and resilience. Remember, deep breathing is a skill that takes practice, but with consistent effort, you can harness its transformative power to navigate life’s challenges with greater ease and clarity.
Comments are closed.